INTRODUCTION
Malignancy is a known pro-coagulant state, predisposing to thrombosis. A number of coagulation abnormalities have been reported to be associated with tumor growth, metastasis, and recurrence in different types of solid tumor including esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, ovarian, lung, and colorectal cancer [1–4].
Tissue factor (TF) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that has a central role in initiating the coagulation cascade [5,6]. TF expression has been identified immunohistochemically in epithelial tissues, specifically the skin, the mucosal surfaces of the gut, and genitourinary system [7]. However, it has also been found to be overexpressed in cancer cells. A direct association between elevated TF expression and advanced stages of malignancy has been confirmed in several different types of cancers [8–11]. More recent studies have suggested that TF expression contributed to metastasis by interfering with cell signaling pathways and presenting the proteolytic activity by the TF/factor VI activated complex. Therefore, increased TF expression is associated with a worse oncologic outcome [12–14].
Fibrinogen, the most abundant plasma coagulation factor, is a key protein in coagulation pathway, clot formation, and wound healing, and is required for platelet aggregation, which is the final step in the coagulation cascade. It has previously been suggested that fibrinogen and platelets have a role in carcinogenesis, and their levels are associated with tumor progression, metastasis, and angiogenesis [15–17]. Furthermore, recent studies have shown that elevated fibrinogen plasma levels and platelet counts are a useful prognostic parameter for recurrence and overall survival [18,19].
Although previous studies suggested a close relationship between colorectal cancer and hypercoagulability, TF was not fully investigated in colorectal cancer. In this study, therefore, we examined the TF expression in patients with non-metastatic colorectal cancer who underwent curative resection. We then analyzed the relationship between TF expression and other coagulation abnormalities, including thrombocytosis and hyperfibrinogenemia, as well as the prognostic factors of tumor recurrence to determine the prognostic role of TF expression.
METHODS
Data pertaining to a total of 305 patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer who underwent curative resection between 2000 and 2007 at The University of Tokyo Hospital were collected retrospectively from a prospectively maintained database. Patients who had a synchronous extracolonic tumor, apparent acute inflammatory disease, severe liver disease, distant metastasis, or preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy were excluded. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The University of Tokyo Hospital and performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The informed consent was waived.
After curative surgery, patients were followed up postoperatively every 3 months for the first 2 years, every 6 months for the next 3 years, and once annually thereafter. Patients were clinically examined and tumor makers were measured at each visit. Full colonoscopy was performed 1 year after surgery, and then once every 3 years. Computed tomography scans were obtained on the basis of individual follow-up regimens (generally every 6–12 months). Recurrences were confirmed radiologically or by biopsy. Locoregional recurrence was defined as tumor regrowth within the pelvis, perineum, or anastomosis site; whereas, distant metastasis was defined as any other recurrence outside of the pelvis.
TF immunohistochemistry
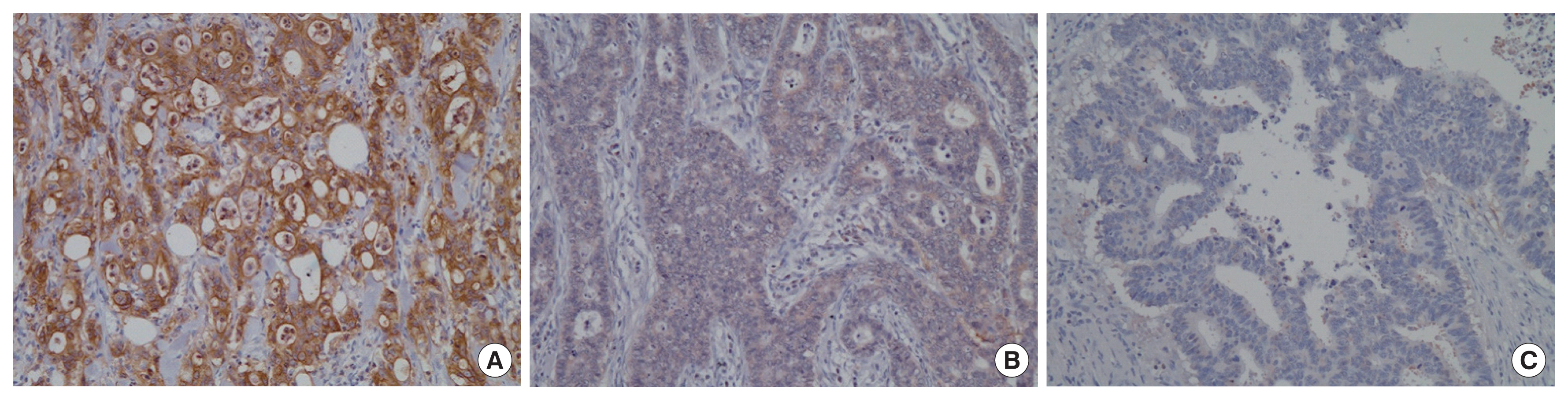
Immunohistochemical staining was performed using formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded, 3 μm-thick colorectal cancer tissue sections. These tissues were deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated in graded alcohols. For antigen retrieval, sections were boiled in 10 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 20 minutes in a microwave oven. Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched using methanol and 3% hydrogen peroxide solution for 15 minutes. After washing with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), the sections were incubated overnight at 4°C with a rabbit polyclonal anti-TF antibody (FL-295, dilution 1:75; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA). After washing in PBS, the sections were incubated with a secondary anti-rabbit biotinylated antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) for 20 minutes at room temperature. After washing again in PBS, these slides were treated with peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin for 10 minutes and developed by immersion in a 0.01% hydrogen peroxide solution and diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride. Light counterstaining was performed with Mayer’s hematoxylin.
Immunoreactivity was assessed by Y.K and K.K who had no knowledge of the associated clinical background. Immunoreactivity of TF was classified as “high” when the cytoplasmic or membrane staining was at least of moderate intensity and occupied more than 75% of the cancer cells in each section.
Statistical analysis
Statistical calculations were performed using statistical software, SPSS version 17.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous data were analyzed by comparing the mean value of each variable between groups by using the Student t-test. Categorical variables were compared using Fisher exact test or the chi-square test, as appropriate. The probability of disease-free survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The log-rank test was employed to compare survival between groups. A P-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
A total of 297 patients were eligible for inclusion in this study. TF expression was high in 257 of the 297 patients (86.5%) (Fig. 1). Table 1 summarizes the associations between TF expression and the clinicopathologic characteristics of the patients. TF expression did not differ significantly according to age, sex, histologic differentiation, depth of invasion, or lymph node metastasis. Further, high TF expression was not significantly associated with the platelet count (P= 0.180) or fibrinogen level (P= 0.281).
The associations between other coagulation abnormalities, thrombocytosis (platelet count ≥ 370× 103/μL) and hyperfibrinogenemia (fibrinogen level ≥ 350 mg/dL), and the clinicopathologic characteristics of patients are summarized in Table 2. In both comparisons, advanced tumor depth was significantly associated with thrombocytosis (P= 0.024) and hyperfibrinogenemia (P= 0.001).
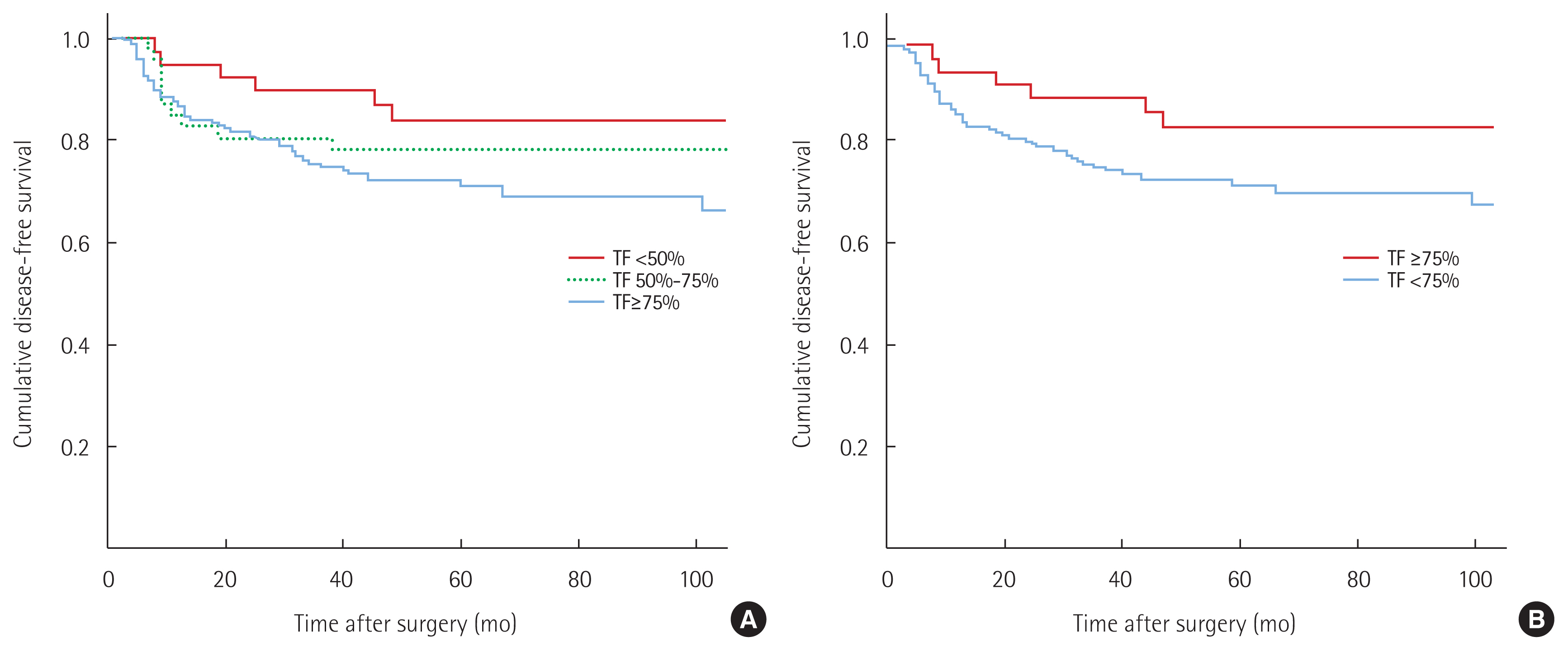
The median clinical follow-up was 69 months (interquartile range, 26–112 months). A total of 73 patients experienced tumor recurrences during the follow-up period, but this occurred more frequently in the high TF expression group than in the low TF expression group (67 patients [26.1%] vs. 6 patients [15.0%], P= 0.167). Fig. 2 shows the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients according to TF expression. The 5-year disease-free survival rate in patients with high TF expression was 72.3%, compared to 83.9% for those with low TF expression although this difference was not statistically significant (P= 0.074). When we sub-classified the proportion of TF positive cells in the section as < 50%, 50%–75%, and ≥75%, TF expression < 50% was associated with a better 5-year disease-free survival rate than TF expression 50%–75% (83.6% vs. 78.2%, P =0.428) or TF expression ≥75% (83.6% vs. 70.8%, P= 0.060), although this difference was also not statistically significant (Fig. 2).
In a univariate analysis, lymphatic invasion (P=0.012), venous invasion (P< 0.001), and lymph node metastasis (P< 0.001) were significantly associated with disease recurrence. Histologic differentiation and TF expression showed the trend, but these were not statistically significant (P =0.092 and P =0.074, respectively). However, thrombocytosis and hyperfibrinogenemia were not significantly associated with recurrence (P= 0.479 and P= 0.234, respectively) (Table 3). Variables in the univariate analysis with a P-value <0.2 were included in the multivariate analysis. In the multivariate Cox hazard model, undifferentiated histologic type (hazard ratio [HR], 2.911; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.308–6.481; P=0.009), venous invasion (HR, 2.784; 95% CI, 1.431–5.417; P =0.003), lymph node metastasis (HR, 2.497; 95% CI, 1.499–4.158; P< 0.001), and high TF expression (HR, 2.446; 95% CI, 1.054–5.674; P= 0.037) were all found to be significantly associated with disease-free survival (Table 4).
DISCUSSION
To assess the risk of relapse among non-metastatic colorectal cancer patients who have undergone curative resection would be of great clinical implications. In this study, we evaluated the prognostic role of coagulation factors, including TF expression, the fibrinogen level, and the platelet count in patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer. We found a significant association between high TF expressions in tumor cells and a high tumor recurrence rate in multivariate analysis. However, TF expression was not correlated with other coagulation abnormalities, including an elevated fibrinogen level and platelet counts, and these were not significantly associated with tumor recurrence.
TF is a 47-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein that is essential for hemostasis. It binds to the coagulation serine protease factor VII/VIIa (FVII/VIIa) to form a protein complex that functions as the primary initiator of coagulation. The TF/FVIIa complex activates both factor X and factor IX and leads to thrombin generation and fibrin formation, both of which are required for physiologic hemostasis. Thrombin also activates platelets through the cleavage of protease-activated receptors [5,6]. In addition to its role in hemostasis, TF has a possible role in cancer growth, metastasis, and recurrence. TF is constitutively expressed in various extravascular cells, but it is also aberrantly expressed in cancer cells and endothelial cells within tumors. It induces angiogenesis by up-regulating vascular endothelial growth factor and down-regulating the angiogenesis inhibitor thrombospondin, in a mechanism that is independent of coagulation [20]. Thus, TF may also contribute to cancer coagulopathy, intratumoral angiogenesis, and tumor progression [8–11]. This is further supported by the findings that a selective reduction in TF expression in colorectal cancer cells using small interfering RNA dramatically reduced tumor growth in a mouse model of malignancy [21].
Previous studies have reported significant association between the immunohistochemical localization of the TF antigen in tumors and poor oncologic outcomes in colorectal cancer. Seto et al. [9] showed that TF expression in colorectal cancer was an independent risk factor for hepatic metastasis and poor prognosis in 67 colorectal cancer patients. Shigemori et al. [22] reported that TF expression was detected in 57% of 79 colorectal tumors and in 88% of 17 liver metastatic tumors from primary colorectal cancer. Findings from these two studies suggest that the immunoreactivity of TF is closely related to metastasis in colorectal cancer. In agreement with these results, our study also showed that high TF expression in colorectal cancer cells was an independent prognostic factor for disease recurrence after adjustment for confounding variables, such as histologic differentiation, venous invasion, and lymph node metastasis in stage II or III colorectal cancer.
There is no standard classification of high TF expression in immunohistochemical staining. Some authors have suggested that high or positive TF expression should be determined on the basis of intensity of staining [23], whereas other authors have suggested the area of the section staining positive for TF should be the basis for determining a high or positive TF expression [15,24]. In this study, we mainly applied the latter, and considered a tumor to be high TF expression when more than 75% of the cancer cells expressed TF. We also supplement our classification for high TF expression by adding to the intensity of staining (at least moderate intensity). In this study, the proportion of patients with high TF expression (86.5%) was higher than reported in previous studies (approximately 50%) [14,23,24]. The discrepancy between our findings for high TF expression and those of previous studies might be explained by our inclusion of only stage II or III colorectal cancer patients, most of whom had T3 or T4 tumors (278 of 297 patients), because previous studies reported that high TF expression was associated with advanced clinical stage, tumor depth, and tumor size [25]. This assumption also might explain the lack of any apparent relationship between TF expression and patient’s clinicopathologic characteristics in this study. Mostly advanced tumor stage (T3 or T4) in this study may have made it more difficult to draw the statistically significant associations between TF expression and those factors.
None of the previous studies addressing TF expression in colorectal cancers investigated the relationship between TF expression and thrombocytosis or hyperfibrinogenemia. However, contrary to our initial hypothesis, we failed to find associations among the coagulation factors. Also, we did not observe any significant association between thrombocytosis or hyperfibrinogenemia and disease recurrence. We consider it also related to selection bias, because thrombocytosis and hyperfibrinogenemia are also known to be related to clinical stage, tumor depth and size [16,18,19]. It was therefore difficult to find a statistically significant relationship between TF expression, serum fibrinogen levels and platelet counts. However, thrombocytosis or hyperfibrinogenemia is known to be a poor prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Therefore, further large cohort study is required to evaluate this relationship.
We found that colorectal patients with high TF expression showed a poorer oncologic outcome than those with low TF expression, suggesting that TF can be a potential target in cancer therapy. Various TF-directed therapeutic agents are being developed, including TF antagonists such as recombinant TF pathway inhibitors and anti-TF antibodies, and other agents that act indirectly on TF expression, such as vitamin D3, retinoids, and heparin [26–28]. Preclinical studies have shown that some of these agents have antitumor and antiangiogenic effects [29]. TF-targeting therapeutic agents have been tested for the treatment of both cancer and non-cancerous diseases. The results of these trials indicate that these agents can destroy tumor vessels by targeting tumor vascular endothelial cells. When administered systemically, these agents can penetrate tumor tissue and kill the tumor cells through leaks in the tumor vasculature. In a mouse model of pulmonary metastasis, inhibition of TF with a variety of agents, such as anti-TF antibodies and a TF pathway inhibitor, reduced tumor metastasis [30].
This study had several limitations, including the selection biases that are inherent in any retrospective analysis. However, we included a relatively high number of patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer, and the follow-up period was relatively long. Because we only included patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer, we did not observe any apparent relationship between TF expression and patient characteristics. However, a number of stage II or III colorectal cancer patients experienced tumor recurrence and death. There is a clinical implication in evaluating prognostic factors for disease recurrence in these patients and it would help to select patients who would benefit from aggressive adjuvant treatment or molecular targeted therapy. Nevertheless, further study is required to evaluate the implication of TF expression in all stages of colorectal cancer. The second limitation was the accuracy with which TF expression was evaluated. However, two pathologists assessed immunoreactivity without knowing the clinical background of the patients, and a Cohen’s kappa test for concordance between the two pathologists gave a value of 0.746, indicating good agreement between them. Therefore, our results suggest that immunohistochemistry is a reliable tool for assessing TF expression in tumors, which in turn could allow the prediction of the oncologic outcome in cancer patients.
In this study, we showed that high levels of TF expression in colorectal cancer cells was associated with disease recurrence in patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer. TF expression could be considered as a prognostic indicator for patients with non-metastatic colorectal cancer. Therefore, the determination of the TF expression status may provide additional prognostic information. However, further studies are needed to establish the underlying mechanism relating TF expression with oncologic outcome. Further studies are also needed to determine the true clinical usefulness of these findings and identify possible roles for TF as a clinical marker and therapeutic target.