림프관 침윤이 있는 stage II 대장암 환자와 국소림프절 전이가 N1인 stage III 환자의 보조적 항암요법의 결과 및 예후
Outcome and prognosis of adjuvant chemotherapy of stage II colorectal cancer with lympatic invasion and stage III with N1 colorectal cancer
Article information
Trans Abstract
Purpose:
Guideline of stage II colon cancer chemotherapy is controversial issue. This study aims to assist in making proper guideline of stage II colorectal cancer chemotherapy.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 137 patients who had colorectal cancer surgery and chemotherapy at Sanggye Paik Hospital, Surgical Department from 2008 to February 2013. We analyzed disease-free survival rate (DFS), characteristics and relationship of stage II (II), stage II with lymphatic invasion (IIL), stage III with N1 (lymph mode involvement number under 3).
Results:
We found new metastasis in 23 patients (liver 11, lung 5, peritoneum 6, bone 1). There is no difference in DFS between II and IIL (P=0.064). But recurrence more frequently appeared with lymatic invasion group. There is no difference in DFS between IIL and III (P=0.083). But cancer stage had not effect to recurrence (P=0.153). In IIL patients, statistically difference did not be shown between oral and intravenous chemotherapy group (P=0.500). But chemotherapy completion group had higher DFS (P=0.001).
Conclusion:
Between II and IIL, DFS did not have difference but low P-value. In consideration of correlation analysis result and DFS between IIL and III, we think their prognosis is not same and completion of chemotherapy influence on good outcome in stage II with lymphatic invasion colon cancer.
서 론
Stage III 대장암에서 fluorouracil (5-FU)에 기초한 보조적 항암화학요법이 사망률을 33%가량 낮추어 준다는 것은 널리 알려진 사실이고 근치적 수술을 시행한 대부분의 환자에게서 시행되고 있다. 그러나 stage II 대장암 환자에 대한 항암제 치료에는 확실한 치료방침이 정해지지 않은 상태이다[1-5]. Quick and simple and reliable (QUASAR) clinical trial은 stage II 대장암 환자에 대한 무작위적인 5-FU 기초 항암치료에서 3% 정도 향상된 낮은 치료성적을 보고하여 모든 stage II 환자에 대한 항암제 치료는 효과적이지 않음을 보여주었다[6]. American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO)나 The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN)는 stage II 환자 중 T4 tumor, 암 분화도가 3 혹은 4, 림프관이나 혈관 침윤, 신경주위 침윤, 장폐색, 장천공, 절제연 양성, 12개 이하의 림프절 획득 등의 고위험군에 대한 보조적 항암요법을 권고하고 있다[3,7]. Stage II와 stage III는 국소림프절 전이의 유무로 결정되는 만큼 림프관 침윤도 중요성을 가질 것으로 판단된다. 림프관 침윤이 있는 stage II와 병기상으로 가장 근접한 stage III 중 N1인 환자의 항암치료 결과와 예후를 조사하고 비교하여 stage II 환자의 치료 방침에 대해 연구해 보고자 하였다.
방 법
2008년부터 2013년 2월까지 인제대학교 상계백병원 외과에서 대장암 수술을 받고 항암제 치료를 시행한 2기 대장암 환자와 3기 대장암 환자 중 N1 병기인 환자 137명을 대상으로 의무기록을 통한 후향적 연구를 하였다. American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) 점수가 4 이상인 환자는 제외하였다. 항암제 치료 후 정기적으로 시행한 computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET) CT 검사에서 수술부위 재발, 간이나 폐 등의 전이가 새로 발생한 경우를 재발로 정의하였고 치료결과로 반영하였다. 일차로 사용한 항암제의 종류, 병기, 국소림프절 전이 개수, 림프절 획득 개수, 국소림프절 전이 개수를 림프절 획득 개수(lymph node harvest)로 나눈 비율(lymph node ratio, LNR), 림프관침윤 유무, 수술 전 carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) 수치를 조사하였다. Chi-square 검증 방법을 이용하여 재발과의 상관관계를 분석하였고 나이, 성별, ASA score, 고혈압 및 심장질환, 당뇨병 유무를 조사하여 각 환자군 간의 특성을 조사하였다. Kaplan-Meier 생존분석으로 무병생존율(disease-free survival rate, DFS)을 조사하였고 log rank test로 검증하였다.
결 과
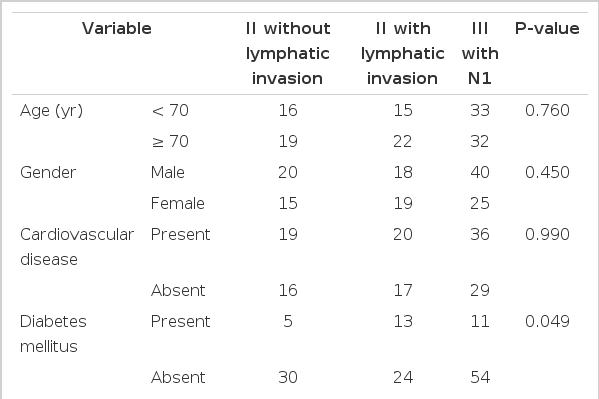
전체 137명의 환자를 림프관 침윤이 없는 stage II (II), 림프관 침윤이 있는 stage II (IIL), 국소림프절 침윤이 3개 이하인 stage III (III)로 나누었고 각각 35, 37, 65명이었다. 근치적 수술 후 모든 환자가 1개월에서 1년간 5-FU 기반의 보조적 항암화학요법을 경구 혹은 정맥주사 방법으로 시행하였다. 항암제치료를 4개월 이상 지속한 경우를 항암제 치료완료로 정의하였다. Stage II 환자에서 재발은 간, 폐, 복강 내 전이가 각각 5, 2, 2명 발생하였다. Stage III 환자에서는 간, 폐, 복강 내, 뼈 전이가 각각 4, 3, 2, 1명 있었다.
각 환자 군의 비교
나이, 성별, T stage, 수술 전 CEA 수치, ASA score, 고혈압 및 심장질환, 당뇨병 유무로 조사한 각 군 간의 성격 차이는 없었다. 항암치료의 완료 여부는 각 군의 차이가 없었지만 stage II 환자는 경구용 항암제를 주로 투여받은 것으로 나타났다(P= 0.001) (Table 1).
재발에 영향을 미치는 인자
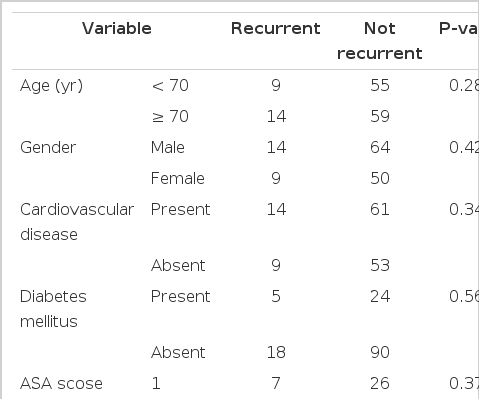
나이, 성별, 고혈압 및 심장질환, 당뇨병, ASA score, T stage, N stage, 림프절 획득 개수, 수술 전 CEA 수치는 재발에 영향을 미치지 않았다. 항암제의 종류 및 투약방법은 재발에 영향을 미치지 않았고 항암치료의 완료 여부가 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보였다(P= 0.002)(Table 2).
무병생존율
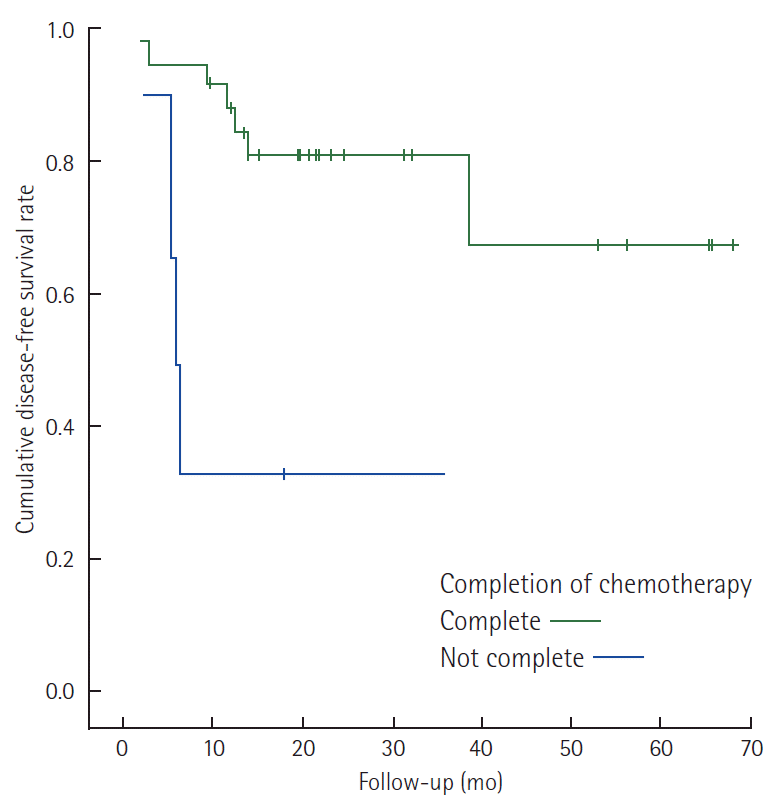
Stage II 환자에서 림프관 침윤 여부에 따른 무병생존율은 통계적으로 유의하지는 않았지만 림프관 침윤이 있는 경우 감소하는 경향이 있었다(Fig. 1). 림프관 침윤이 있는 stage II와 N1 stage III 환자에서 항암제의 종류에 따른 무병생존율의 차이는 보이지 않았으나 항암제 투여 완료 여부에 따른 차이는 통계적으로 유의하였다(Fig. 2). 특히 림프관 침윤이 있는 stage II 환자를 대상으로 한 경우 그 차이가 더욱 현격하게 나타났다(Fig. 3).
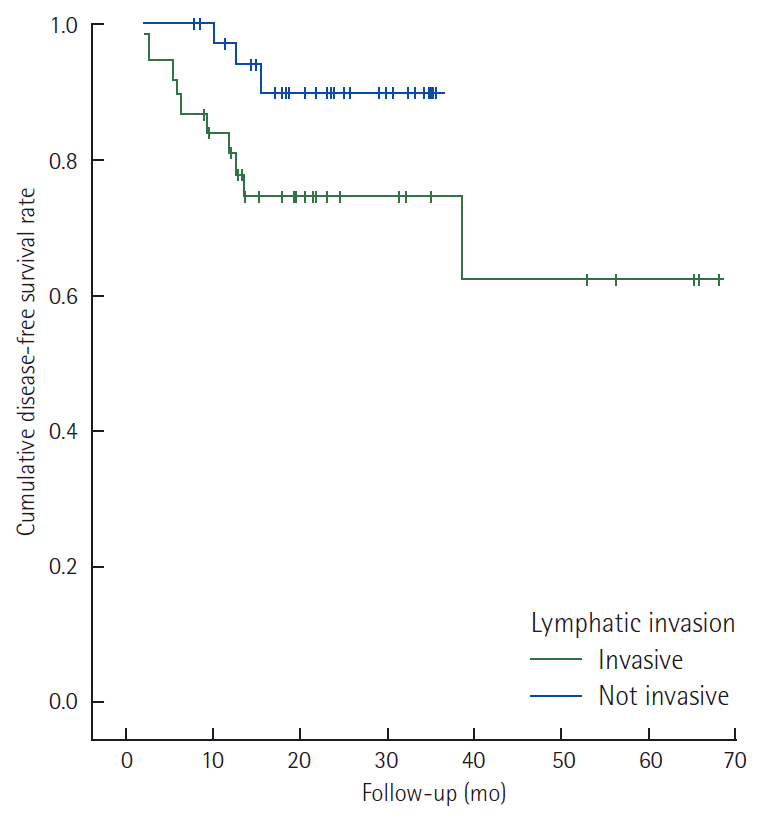
Disease-free survival rate curves of stage II colorectal cancer patients with lymphatic invasion and without invasion (Log rank P = 0.064).
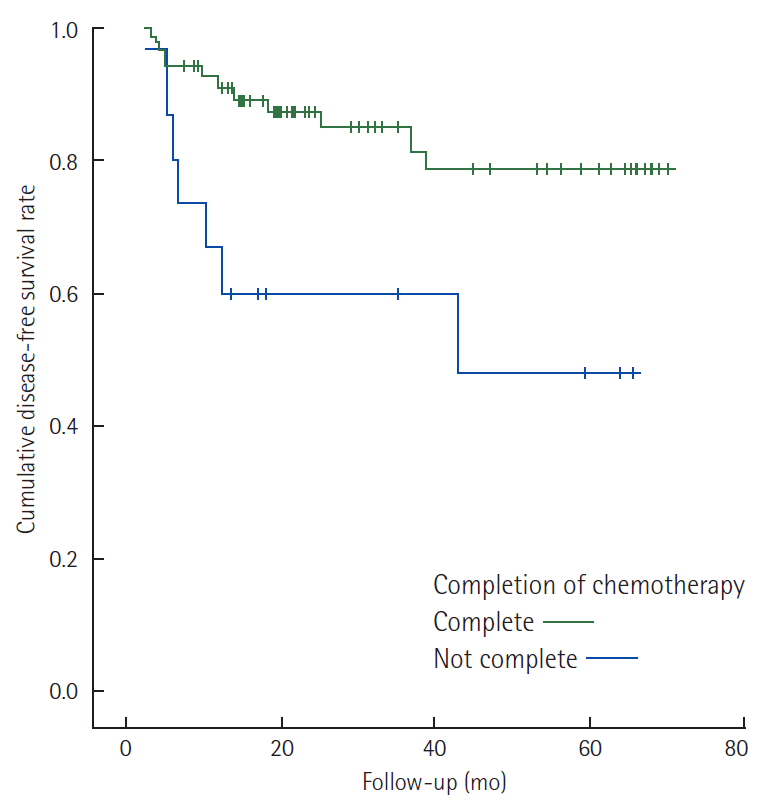
Disease-free survival rate curves of stage II colorectal cancer patients with lymphatic invasion and stage III with N1 (Log rank P = 0.005).
고 찰
1990년 Motel 등[1]은 3기 대장암 환자에서 5-FU에 기초한 보조적 항암화학요법이 사망률을 33%가량 낮추어 준다고 보고하였다. 2004년 The MOSAIC trial에서는 5-FU/leucovorin (LV)/oxaliplatin의 향상된 치료성과를 보고하였다[2]. 이후 3기 대장암 환자에 대한 보조적 항암요법은 합당한 근거를 가진 치료방침을 확립하였다. 그러나 2기 대장암 환자에 대하여서는 아직 합당한 근거를 가진 치료방침이 확립되지 않은 상태이다[3-5]. Stage II 대장암 환자는 수술만으로도 75%-80%의 높은 5년 생존율을 보인다[3]. 2007년 QUASAR (quick and simple and reliable) clinical trial에서는 2기 대장암환자에 대한 무작위 연구를 시행하였다. 5-FU에 기초한 보조적 항암요법에서 3% 향상된 정도의 낮은 치료성적을 보고여 모든 2기 대장암환자에 대한 항암제치료는 효과적이지 않음을 보여주었다[6]. ASCO에서도 고위험군에 대한 보조적 항암요법만 권장하고 있다[3]. NCCN는 2기 대장암 환자 중 저위험군 환자에 대하여는 경과관찰을 하거나 5-FU/LV, capecitabine 항암화학요법을 권고하였고 고위험군 즉, T4 stage, 암 분화도가 3 혹은 4, 림프관이나 혈관 침윤, 신경주위 침윤, 장폐색, 장천공, 절제연 양성, 12개 이하의 림프절 획득 등의 경우에서는 5-FU/oxaliplatin, capecitabine/oxaliplatin 을 고려할 것을 권고하고 있다[7].
American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) cancer staging 7판에서 대장암 2기와 3기는 국소림프절 전이의 유무로 정해진다. 림프절은 병기결정과 그에 따른 치료, 예후 예측에 매우 중요한 인자이다[8]. Akagi 등[9]은 림프관 침윤은 국소림프절 전이와 비슷한 양상을 보이고 독립적인 예후 예측인자가 될 수 있다고 하였다. ASCO나 NCCN은 림프관 침윤을 재발의 고위험 인자로 분류하고 있지만 합당한 근거가 될 만한 무작위 대조군 연구는 없는 상태이다[3,7]. 본 연구에서는 대장암 2기 환자 중 림프관 침윤이 있는 환자(IIL)와 없는 환자(II)의 무병생존율의 차이는 보이지 않았지만(P=0.064) 유의확률이 낮았고 상관관계 분석에서는 림프관 침윤이 있는 군에서 재발이 잘 발생하였다(P= 0.045). 림프관 침윤이 있는 2기 대장암 환자(IIL)와 N1인 3기(III) 대장암 환자의 비교에서 두 군 간의 무병생존율 차이는 보이지 않았고(P= 0.083) 상관관계 분석에서 병기가 재발에 영향을 미치지 않았다(P= 0.154). 이 결과로 보아 림프관 침윤이 있는 2기 환자의 예후는 림프관 침윤이 없는 2기보다는 N1인 3기 환자와 더 유사한 경향을 보인다고 할 수 있을 것이다. 본 연구에서 경구 항암제군과 비경구 항암제군 간의 무병생존율 차이는 보이지 않았다. Lembersky 등[10]은 UFT+LV이 5-FU 정맥투여와 비교하여 DFS, OS에서 차이가 없다고 하였고, Douillard 등[11]은 같은 효과와 경구 항암제의 안전성, 편의성을 보고하였다. NCCN의 권고에 따르면 림프관 침윤이 있는 환자에서는 5-FU/oxaliplatin, capecitabine/oxaliplatin 항암치료를 권고하고 있다. 그러나 본 연구의 결과와 상기 연구들의 결과를 보았을 때 전신상태가 좋지 않거나 5-FU/oxaliplatin, capecitabine/oxaliplatin 항암제에 부작용이 많은 환자 등 비경구 항암제의 사용이 어렵다고 판단되는 환자에게서 경구 항암제의 사용은 예후에 악영향을 미치지 않을 것으로 판단된다. IIL에서 일차 항암제치료를 마친 군의 DFS가 높았고(P=0.006, 54% vs. 87%), IIL과 III를 합친 군에도 일차 항암제치료를 완료하였을 때 DFS가 높았다(P= 0.005, 45% vs. 85%). 대장암 2기 환자에서는 높은 5년 생존율로 인하여 환자가 힘들어하거나 전신상태가 약간 나빠졌을 때에도 항암제 치료를 종료하는 경우가 종종 있었디. 림프관 침윤이있는 환자들에서는 4개월 이상 항암제 치료를 지속하는 것이 예후에 도움이 될 것으로 판단된다. 획득된 림프절 개수가 중요한 예후인자라는 보고가 있다[8,12]. NCCN 등[7]은 12개를 획득된 림프절의 적절한 개수로 보았고 Rivadulla-Serrano 등[13]은 14개를 적절한 개수로 보았다. 본 연구에서는 IIL과 III을 합한 군에서 12개 이하의 림프절 획득 시 재발이 잘 발생하였다(P= 0.027). 수술 시 가능한 많은 림프절을 절제하는 것이 예후에 영향을 미칠 것으로 생각된다.
대장암 2기 환자에서 림프관 침윤이 있는 환자와 없는 환자의 예후는 다른 것으로 생각된다. 림프관 침윤이 있는 2기 대장암 환자는 항암치료를 완료하는 것이 예후에 좋을 것으로 생각되고 경구 항암제의 효과는 정맥주사 방법 항암제에 비하여 나쁘지 않은 것으로 판단된다.
Notes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 2010 Inje University research grant.